Heavy metal contamination in soil is of great environmental concern due to rapid urbanization and industrialization in China. Phytoremediation technology is a feasible way to remove heavy metals from farmland, especially for cadmium pollution. Application of plant growth regulators (PGRs) is an alternative strategy, which has been considered to potentially enhance the efficiency of phytoextraction of heavy metals by plants.
This study compared the effect of foliar application of 11 plant growth regulators on cadmium absorption by amaranth, and revealed the mechanism of plant growth regulators promoting amaranth to repair polluted soil. Effects of gibberellin and compound nitrophenol sodium on the growth and development, chlorophyll content, antioxidant enzyme activity, cadmium extraction capacity and microdistribution of amaranth in cadmium polluted soil.
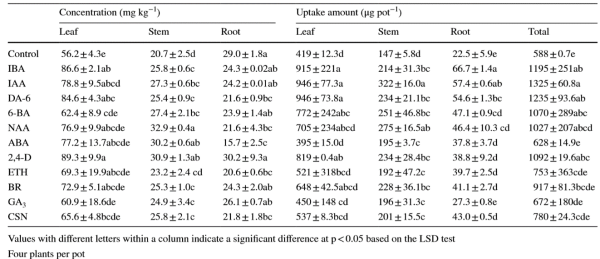
The effect of growth regulators on biomass depends on their own types, among which indole-3-butyric acid is the most effective. The addition of PGRs increased Cd extraction efficiency, with their effect decreasing in the order: IAA>DA-6>IBA>2, 4-D>6-BA>NAA>BR>CSN>ETH>GA3>ABA.
The application of PGRs increased cadmium content in leaves and stems, but decreased cadmium content in roots (except 2,4-D). Exogenous PGRs increased the activity of SOD and cat, decreased the content of MDA, and SEM-EDS further confirmed that indole-3-butyric acid or diethyl hexanoate could promote the accumulation of Cd in the upper and lower epidermal cells of amaranth and the migration of Cd from the root to the leaf. Therefore, it can be seen that the PGRs can be used as an effective regulator to improve the phytoextraction efficiency.
The relevant results of this study have been finished by SUN Shuo (First author), Dr. ZHUANG Ping (corresponding author) and Prof. LI Zhian (corresponding author) and other colleagues from South China Botanical Garden of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and recently published in Plant Growth Regulation, entitled " Exogenous plant growth regulators improved phytoextraction efficiency by Amaranths hypochondriacus L. in cadmium contaminated soil". For details, please refer to: https://rd.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10725-019-00548-5.
Table. Effect of plant growth regulators on Cd concentration in the tissues of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. (Mean±SD, n=3, dry mass)
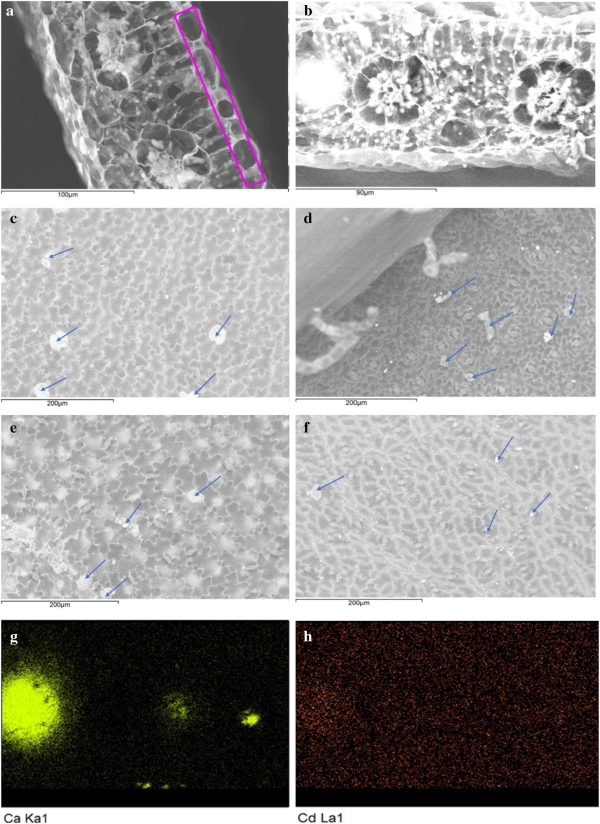
Figure. Backscattered electron image of scanning electron micrographs in leaf of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. a Cross section of leaves under IBA treatment, b cross section of leaves under DA-6 treatment, c upper epidermis of leaves under IBA treatment, d lower epidermis of leaves under IBA treatment, e upper epidermis of leaves under DA-6 treatment, f lower epidermis of leaves under DA-6 treatment, g mapping image of Ca (h) mapping image of Cd.