Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Aiton) Hassk., also knownd as Rose myrtle, is distributed in the hilly areas of Taiwan, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Lingnan region. R. tomentosa is a medicinal and ornamental plant, and its sweet fruit is edible.
Liyun Zhao, Ph.D. student of the Natural Products Chemical Biology Research Group of South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, under the guidance of Prof. Shengxiang Qiu and Associate Professor Haibo Tan, studied the antibiotic-resistant bacteria activity and mechanism of the antibacterial active ingredient, rhodomyrosone B from R. tomentosa. It was found to have strong antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE). It was also found that the antibacterial mechanism of rhodomyrosone B and its derivatives was to change the membrane potential of the resistant bacteria. By screening a series of synthetic derivatives for anti-resistant bacteria activity and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies, more active (up to 4-5 times) lead compounds were obtained and their antibacterial activity verified in vivo experiment.
Related research results have been published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology (228, 2019, 50-57) and Med. Chem. Commun., (DOI: 10.1039/C8MD00257F). We also has obtained the national invention patent authorization ("Myrtle ketone compounds and their application in the preparation of antibacterial drugs", patent number: ZL201510182272.2). The team’s research results in rhodomyrosone B and plant-derived antibiotics provide a material basis for subsequent research on innovative anti-drug resistant antibiotics.
This work was financially supported by the Strategic Resources Service Network Program on Plant Genetic Resources Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. ZSZC-005), National Natural Science, ‘Twelfth Five-Year’ National Science and Technology Support Project of China (2015BAD15B03), Foundation of China (No. 81502949), Guangdong Province Science and Technology Project (No. 2016A010105015), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2015A030310482).
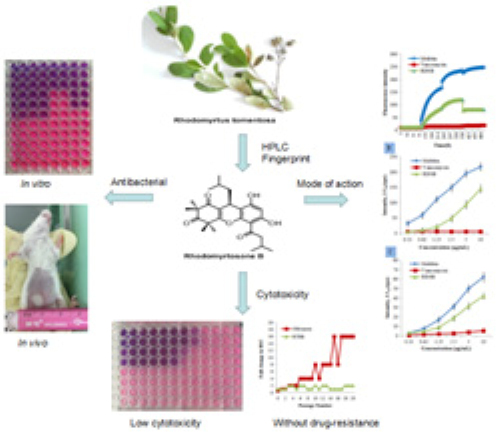
Fig.1 Rhodomyrtosone B, a membrane-targeting anti-MRSA natural acylgphloroglucinol from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa.
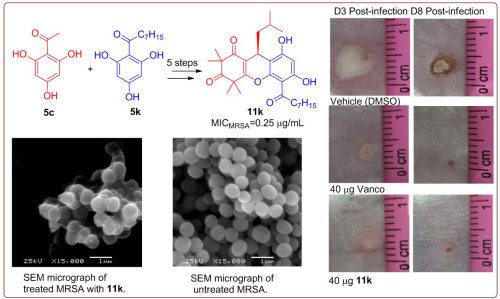
Fig.2 Structural optimization and antibacterial evaluation of rhodomytosone B analogues against MRSA strains.

