The South China Botanical Garden published a new genus of Asteraceae — Qineryangia Y. S. Chen & L. S. Xu.
The tribe Cichorieae of the family Asteraceae comprises approximately 95 genera and 2500 species, distributed widely in the Northern Hemisphere. In China, there are about 35 genera and 388 species. Many of these plants possess significant edible, medicinal, and ornamental value, such as Lactuca, Cichorium, and Taraxacum. The Cichorieae plants exhibit diverse habitats and morphological variations, presenting challenges in their description and classification due to disputed genus boundaries.
The subtribe Crepidinae, within the Cichorieae, is the largest subtribe comprising approximately 360 species, mainly distributed across the Eurasian continent. Flora of China (2011) documented about 230 species belonging to 17 genera, with China recognized as the center of diversity for Crepidinae. However, due to the complexity of morphological characteristics, lack of molecular data, and inadequacy of genetic information obtained through traditional (Sanger) sequencing methods, the phylogenetic relationships within this group have remained unresolved. Scholars such as Cassini, Hoffmann, and Stebbins have proposed entirely different delineations and subdivisions of this subtribe based on morphological, cytological, and molecular biological evidence. Therefore, systematic taxonomic research on Crepidinae necessitates more representative sampling, more effective data acquisition techniques, and analytical methods.
Plant Diversity and Taxonomic Research Group (PI: Professor You-Sheng Chen) of South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, conducted extensive specimen examination and field surveys to collect research materials for important groups within the Crepidinae and its sister groups. They utilized Hyb-Seq to obtain nuclear and chloroplast genome data and conducted phylogenetic analysis, incorporating morphological evidence, to propose a new classification framework comprising 29 genera within the Crepidinae. In this system, the subtribe Chondrillinae is merged into the subtribe Crepidinae. Additionally, the genus Mojiangia, whose systematic position was previously uncertain, is confirmed to belong to the base of the subtribe Crepidinae, forming a relatively independent branch. Furthermore, during the research process, an unknown plant species was discovered, distributed only in Baoxing County, Sichuan Province, China. It exhibits distinct characteristics of the Crepidinae, with yellow ligulate flowers. The plant has large involucre, numerous phyllaries and ligulate flowers, with wavy margins of phyllaries imbricate arrangement loosely. This combination of features does not belong to any genus within the Crepidinae. Subsequent morphological comparisons and molecular phylogenetic analysis confirmed this species as a new undescribed species, constituting a monospecific genus, and showing close affinity with taxa such as the genus Crepidiastrum and Youngia.
Therefore, based on comprehensive evidence from morphology, palynology, and molecular systematics, researchers have described a new species, Qineryangia baoxingensis Y. S. Chen & L. S. Xu, and established a new genus, Qineryangia Y. S. Chen & L. S. Xu. The genus name pays tribute to the Chinese botanist Professor Qin-Er Yang, in recognition of his contributions to the study of plant classification in China. This study represents the first utilization of Hyb-Seq to obtain genomic data for groups such as the Crepidinae, yielding a high-resolution molecular systematics framework for this subtribe and providing crucial data and insights for phylogenetic studies within Crepidinae, Cichorieae, and Asteraceae. The related research findings, titled "Qineryangia, a new genus from the Hengduan Mountains and new insights into the phylogeny of the subtribe Crepidinae (Cichorieae, Asteraceae)," have been published in Journal of Systematics and Evolution. Assistant Professor Lian-sheng Xu is the first author of the paper, and Professor You-sheng Chen is the corresponding author. This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, and and the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project. The article link is: https://www.jse.ac.cn/EN/10.1111/jse.13066
Author: The team of Yousheng Chen from the Botany Centre of South China Botanical Garden, Yousheng Chen,email:yschen@scbg.ac.cn , tel:13922723952.
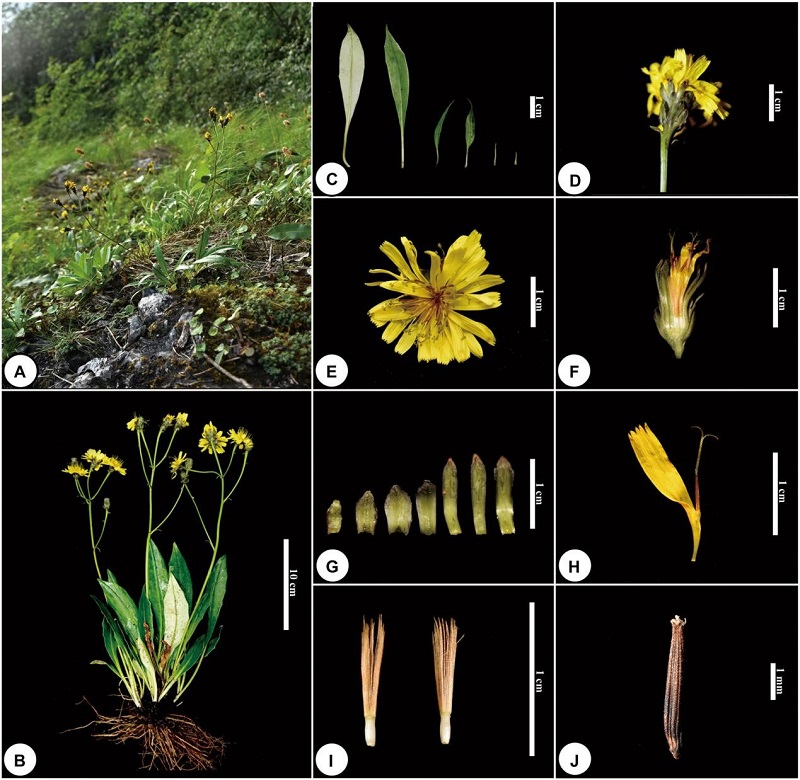

Figure 1. Morphological characteristic of Qineryangia baoxingensis.
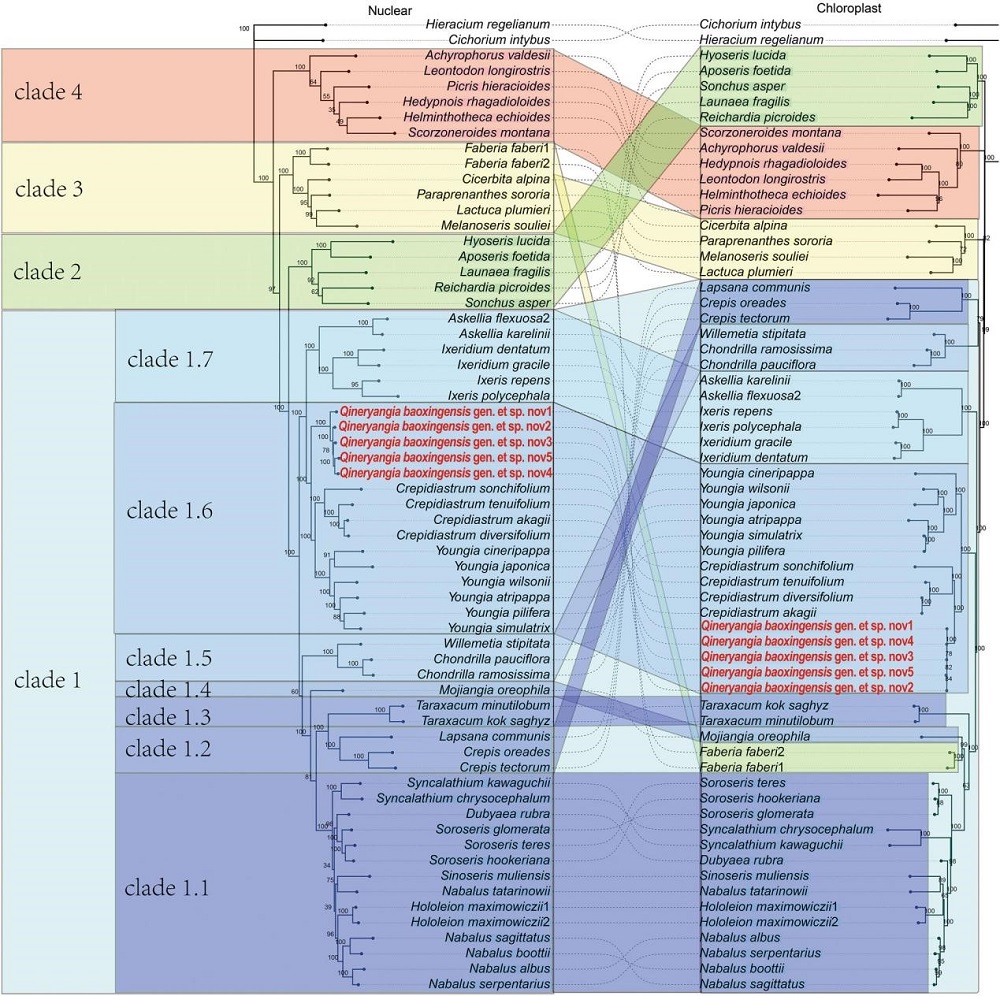
Figure 2. Phylogenetic trees of subtribe Crepidinae based on 726 nuclear loci (left) and on 198 chloroplast sequences (right),
show the systematic position of Qineryangia baoxingensis (Qineryangia).
File Download: