New progress on leaf phosphorus-allocation strategies of deciduous oaks in China
Allocation patterns of leaf phosphorus (P) reflect trade-off strategies of plants to maintain and/or enhance P-use efficiency under diverse environments. Understanding the variation in leaf P-allocation across geographic ranges is crucial for predicting the changes in plant growth and ecosystem functioning, and the potential geographic shifts of plants.However, up to date, most studies remain confined at regional scales and mainly scatter across different families and genera, which hinder this deeper understanding how leaf P-allocation of congeneric species affects their adaptive strategies and geographic ranges.
Researchers from the Restoration Ecology Group in South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, studied the variation of five P fractions and their drivers in four deciduous oaks (Quercus) with either wide (Q. acutissima and Q. variabilis) or narrow (Q. fabri and Q. mongolica) distribution ranges in subtropical and temperate forests across China. They found that the deciduous oaks in subtropical forests had higher proportions of lipid, nucleic acid and residual P but lower proportion of metabolite P than those in temperate forests; leaf P-allocation patterns among oak species were convergent in subtropical but divergent in temperate forests; global change factors (mean annual temperature, nitrogen deposition rate and aridity index) rather than soil P concentrations determined the leaf P-allocation patterns across China; those dominant factors had greater effects on P-allocation of narrow-ranging oaks than on that of wide-ranging oaks (Figure). Those findings unravel plastic leaf P-allocation strategies of deciduous oaks growing in habitats with contrasting P availability, and highlight the potential impacts of P-allocation strategies on the future distribution or habitat differentiation of congeneric species (narrow- vs. wide-range) in the context of global change.
The results titled by “Contrasting leaf phosphorus-allocation strategies between subtropical and temperate oaks” was published in Plant, Cell & Environment. Article link: https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.70368
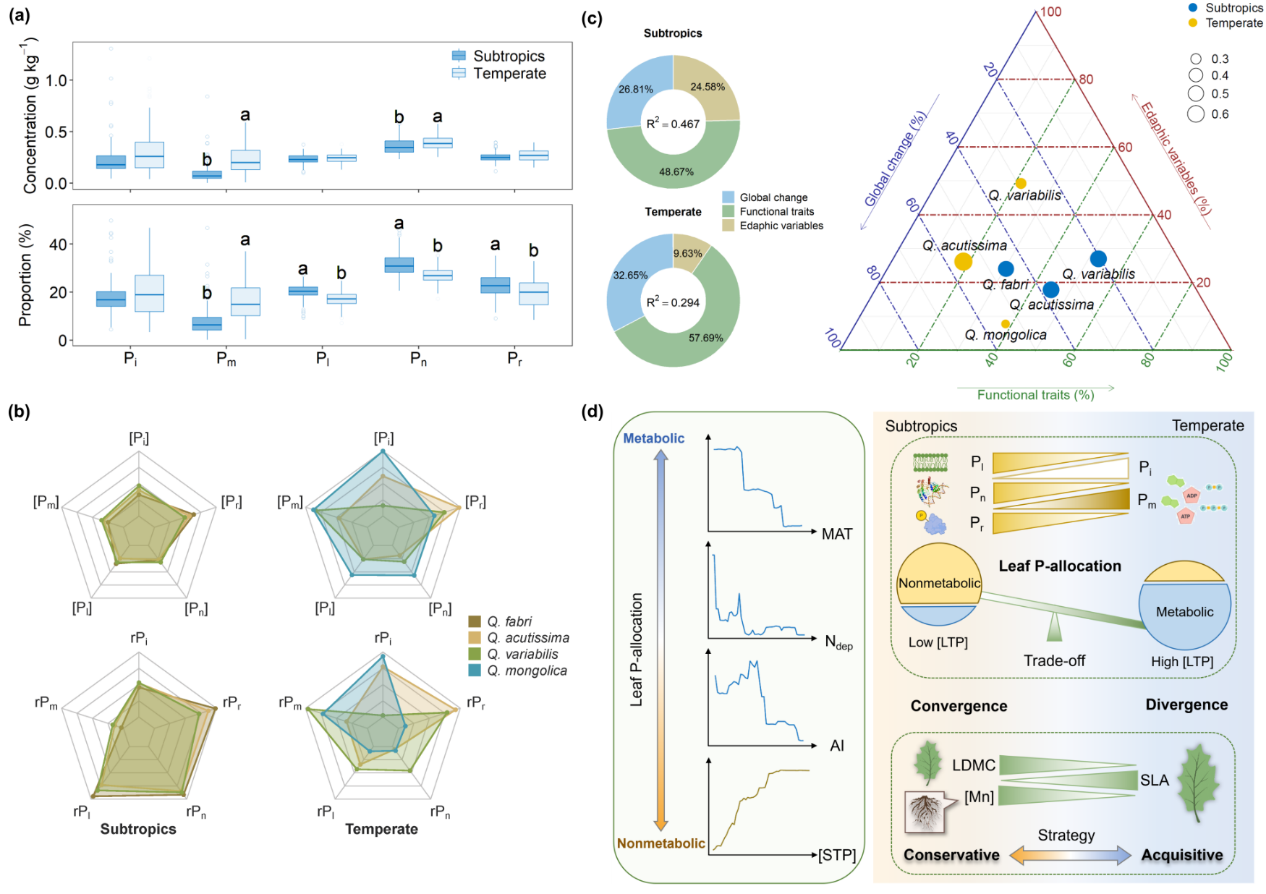
Figure. Spatial patterns and regulatory mechanisms of leaf phosphorus-allocation strategies in deciduous oaks.
File Download: