News
-
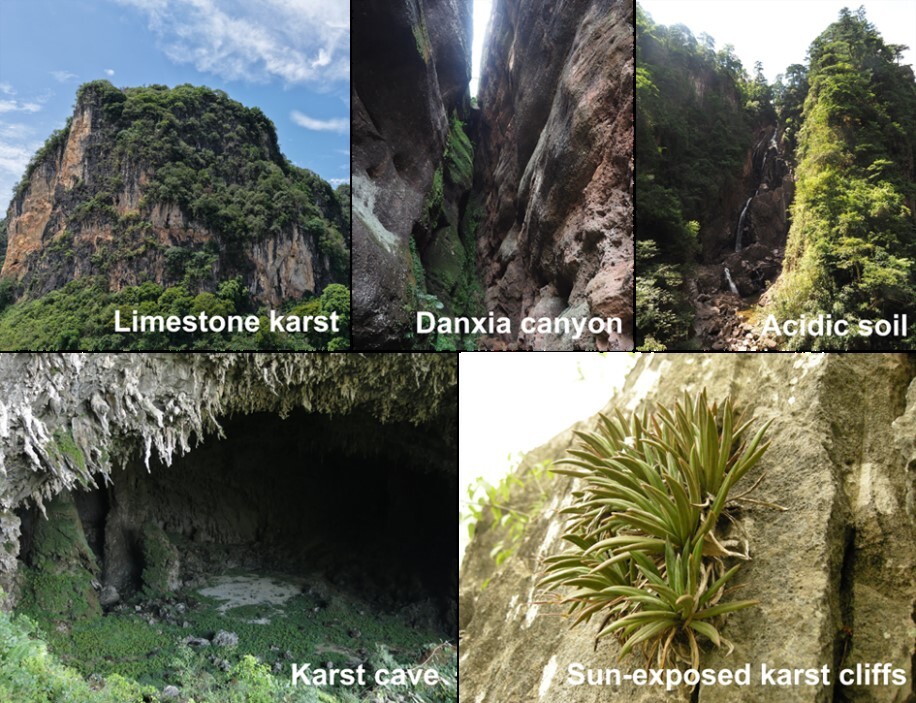
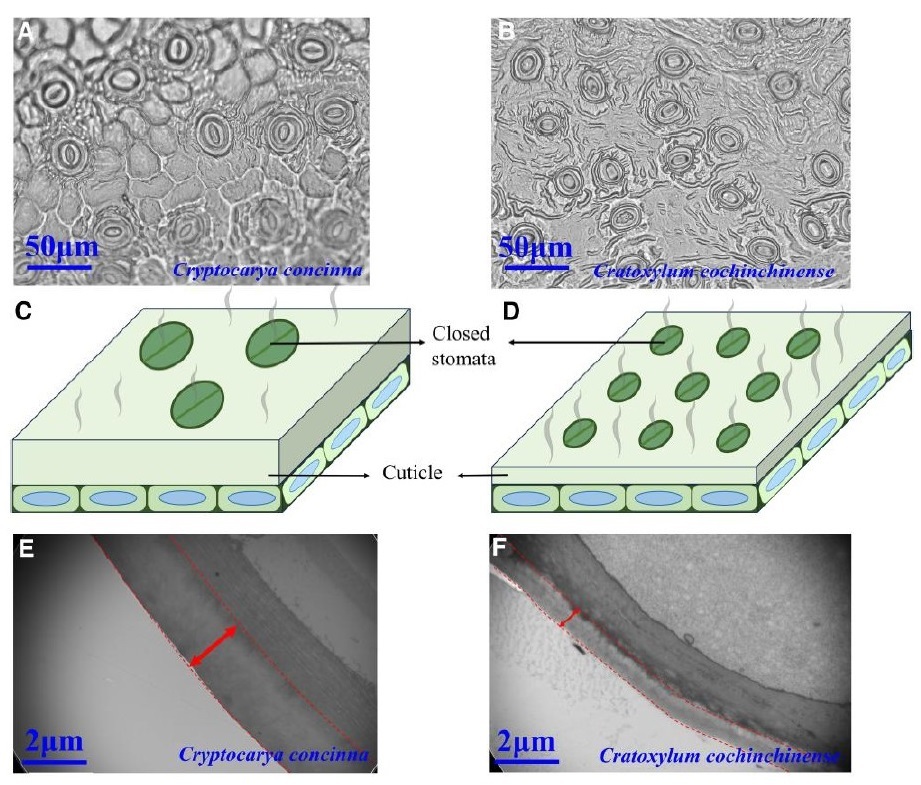
2026-01-01Restoration Ecology Research Team Reveals Interspecific Variation in Minimum Leaf Conductance Among Dominant Woody Species in Subtropical Forests and Its Key DriversThe cuticle determines minimum leaf conductance, with light requirement strategies driving species differences in cuticle thickness. Global climate change has profoundly altered terrestrial plant water relations. In particular, shifts in precipitation regimes, rising temperatures, and increasingly frequent extreme drought events pose serious challenges to plant growth and survival. Minimum leaf conductance (gmin) characterizes the rate of water loss after stomatal closure and...Read More
-
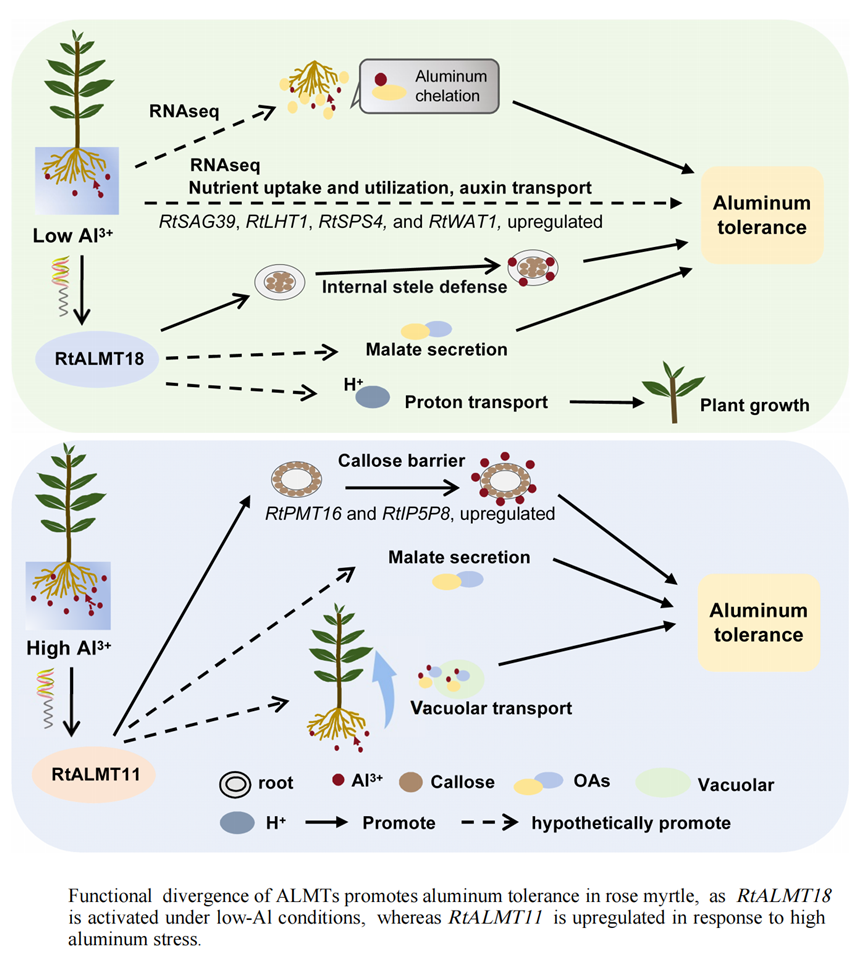
2025-12-30Researchers uncover the molecular mechanism underlying rose myrtle's adaptation to acidic aluminum-stressed soilALMT family functional divergence empower Rhodomyrtus tomentosa turns aluminum stressor into growth promoter. Acidic soils, accounting for over 50% of global potential cultivable land and serving as the core matrix for agricultural production in southern China, release soluble aluminum ions (Al³⁺) that damage plant roots and limit crop growth. Notably, Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (rose myrtle) not only tolerates high-aluminum environments but also uses low ...Read More
-
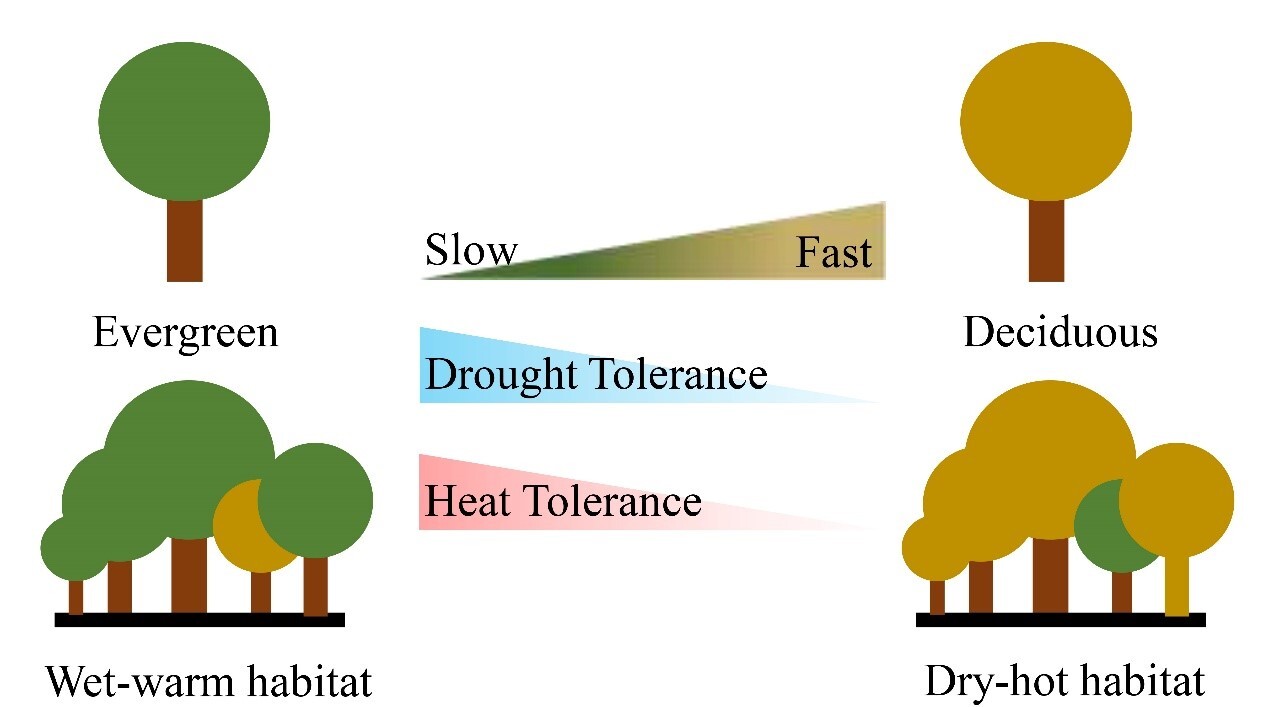
2025-12-30Reveals that leaf economics is the central hub to link drought and heat toleranceLeaf economics is the central hub to link drought and heat tolerance, with heat tolerance primarily influenced by leaf habit, whereas drought tolerance and economics affected by both leaf habit and habitat. This study provides key evidence that leaf economic traits have the potential to predict both drought and heat tolerance of plants under fut... The combined stress of drought and high temperature is posing a growing threat to plants. Drought directly affects plants by breaking down the water transport system, and indirectly affects carbon assimilation process. Elevated temperatures can damage photosynthetic machinery and scorch leaves, which can impair carbon-dependent development of ot...Read More
-
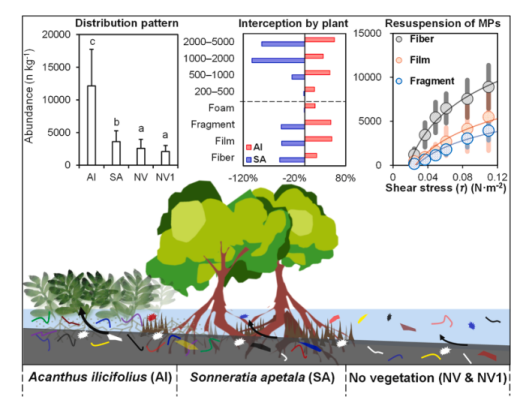
2025-12-25Global Change Ecology Research Team Reveals the Source-Sink Dynamics of Microplastics in Mangroves and Their Driving MechanismsThe interception of MPs by mangrove during their seaward transport results in a mass imbalance between input into rivers and output to the sea, underscoring the role of mangroves as a major sink for MPs. Conversely, hydraulic disturbances-induced sediment resuspension converts mangrove into a secondary contamination source for the water column. Recently, the Global Change Ecology Research Team from the South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published their latest research findings on Journal of Hazardous Materials, offering a new perspective on the source-sink dynamics of microplastics (MPs) in mangrove ecosystems. Combining field investigations and indoor resuspens...Read More
-
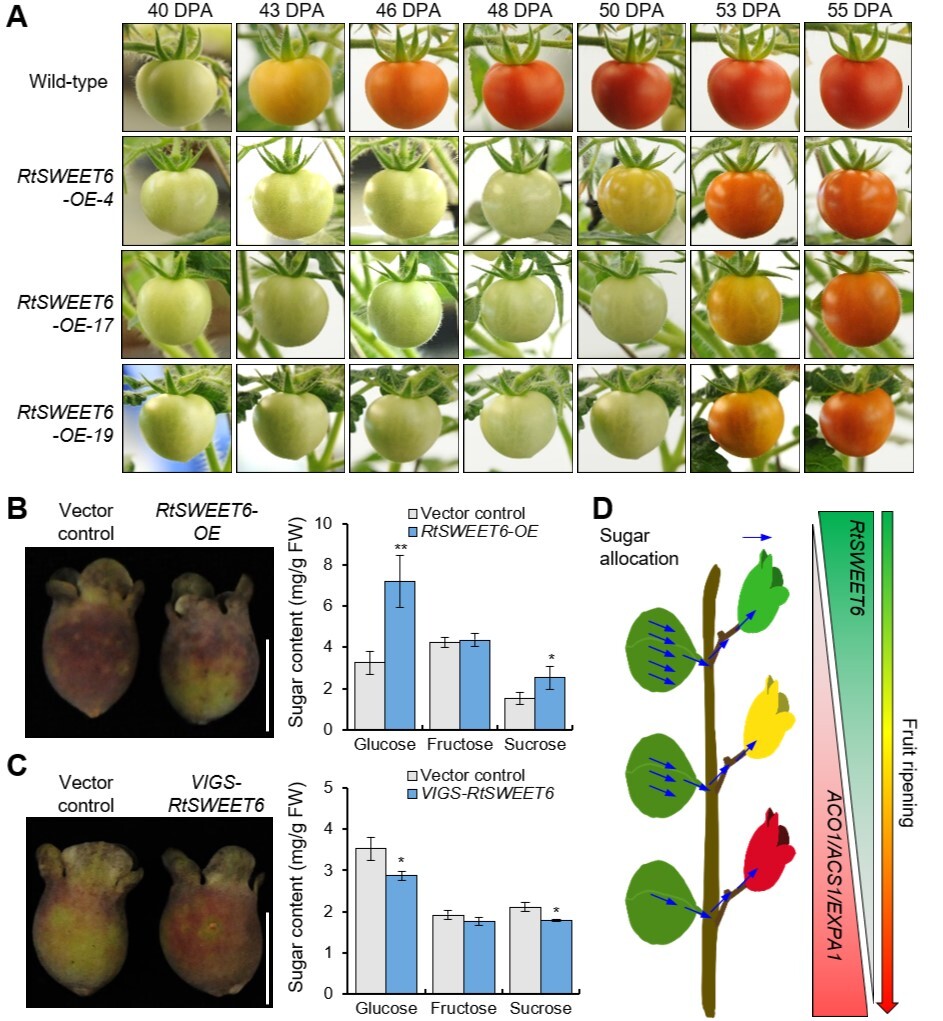
2025-12-25New progress on the key regulatory mechanism of sugar accumulation and ripening in rose myrtle fruitsThe fruits of Rhodomyrtus tomentosa, containing abundant bio-active compounds, are usually used for fresh eating and food processing. Researchers reveal that RtSWEET6 is a hexose transporter that regulates sugar allocation and fruit ripening, providing a strategy for improving sugar content and extending the shelf life of fresh fruits. Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Ait.) Hasskis an emerging berry fruit crop widely distributing across tropic and subtropic regions. The fruits of R. tomentosa, which contain abundant anthocyanins and sugar,are consumed freshly or processed as beverages, jams, and jellies. Owing to the thin skins and soft flesh, the berries decay rapidly after ripening an...Read More
-
2025-12-25Primulina pan-genome reveals differential gene retention following whole-genome duplications and provides insights into edaphic specializationFeng et al. assemble seven high-quality genomes and construct a genus-wide Primulina pan-genome. Lineage-specific whole-genome duplications show biased duplicate loss in large gene families but preferential retention of transcription factors. Pan-genome analyses reveal that genome downsizing, biased retention following polyploidy, and adaptive e... Edaphic specialization—the adaptation of plants to unique or extreme soil environments—offers critical insights into ecological differentiation and the evolutionary mechanisms that drive biodiversity, yet its genomic basis remains poorly understood. Primulina, a genus of Gesneriaceae with >200 species endemic to extreme soils, is predominantly...Read More
-
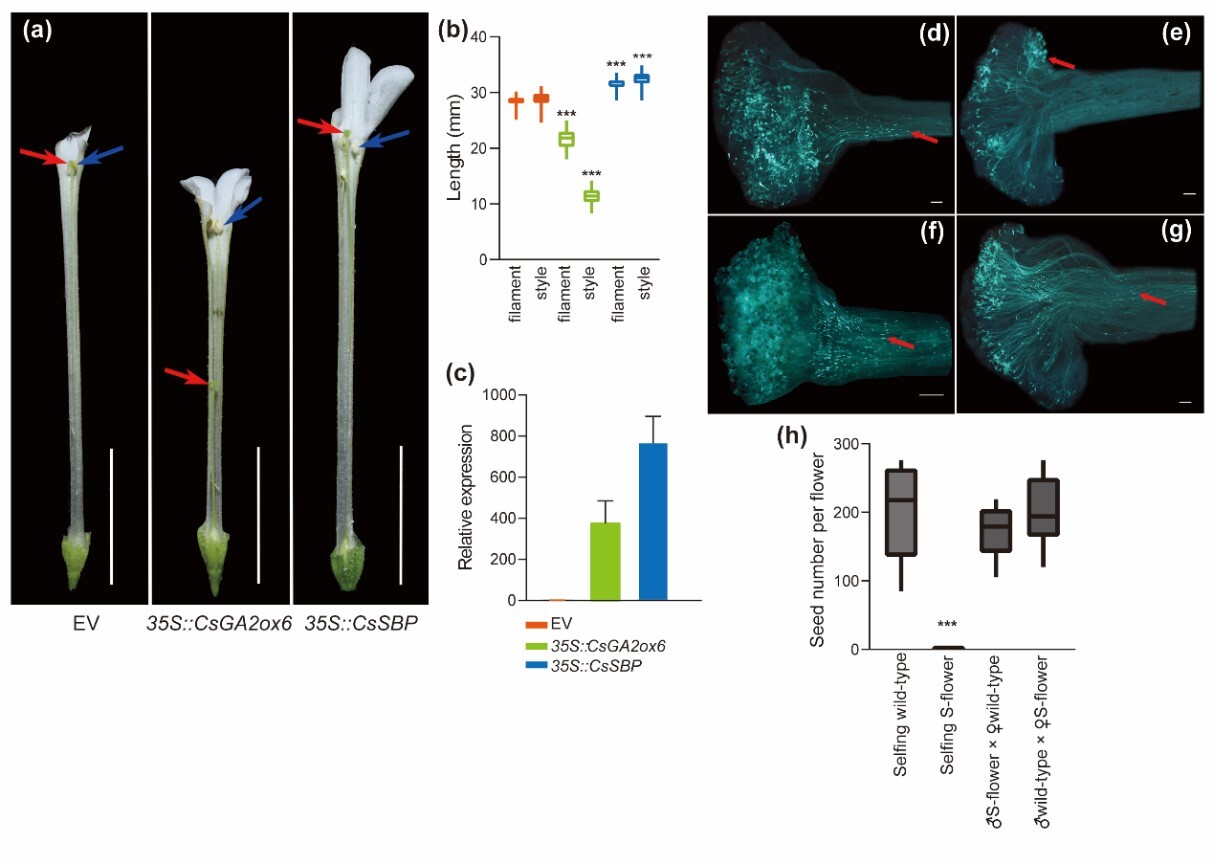
2025-12-18New Progress in the Molecular Mechanisms of HeterostylyResearch on the distylous Cordia subcordata provides insights into the convergent evolution of the hemizygous S-locus and establishes a link between style-length regulation via CsGA2ox6-mediated gibberellin deactivation and the potential control of self-incompatibility. Since Charles Darwin published The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species in 1877, heterostyly has served as a classic model system in studies of plant reproductive biology. Heterostyly is a floral polymorphism controlled by a S-locus supergene and is characterized by the presence of two (distyly) or three (tristyly) floral mor...Read More
-
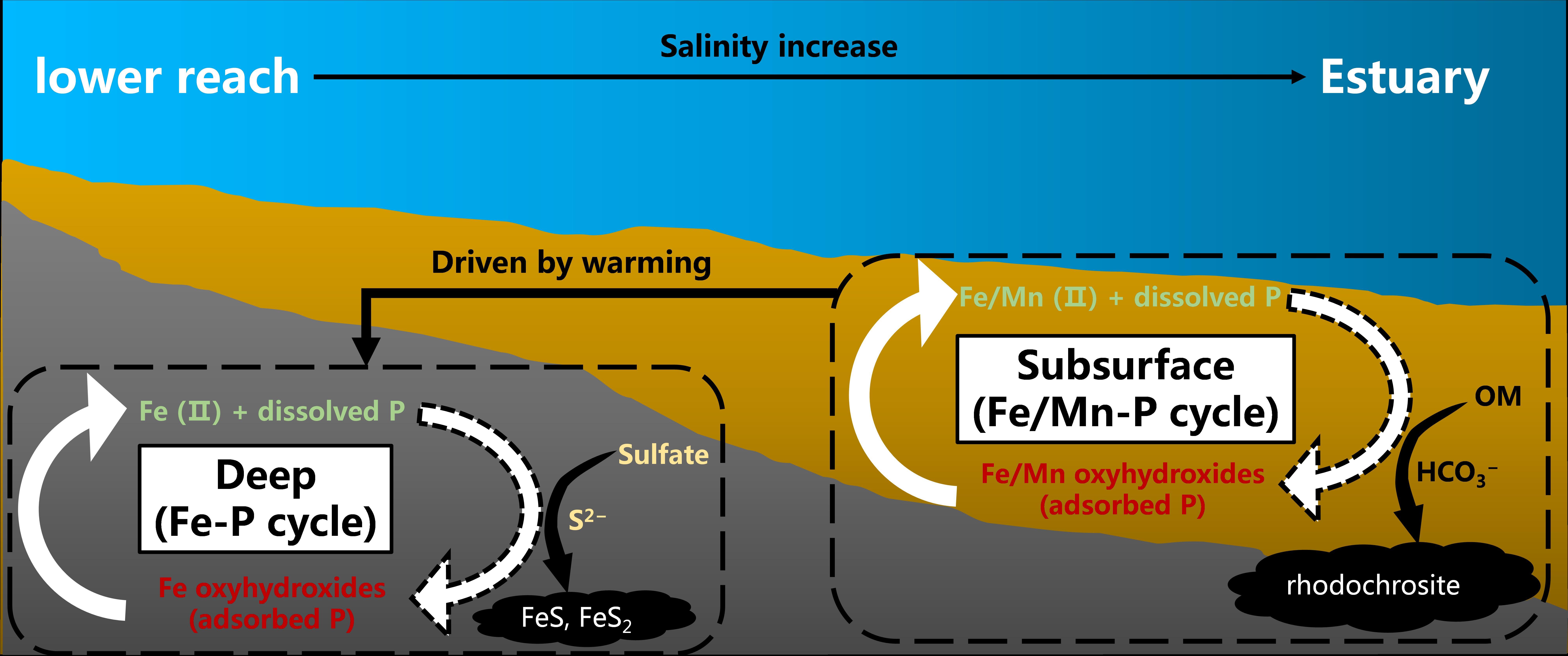
2025-12-18From field observations to laboratory simulations: Warming promotes manganese-phosphorus remobilization in estuarine sedimentsIn this work, the characteristic mechanisms of P remobilization in sediments of the Jiaomen Channel were explored using sequential extraction method, diffusive gradients in thinfilms (DGT) device, and pore-water sampler. The results showed that Intense organic matter mineralization removes dissolved Mn from pore water as carbonates, triggering a... Recently, Lei Gao’s research team from the South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has published a research paper on Journal of Hydrology, exploring the dynamic mechanism of phosphorus (P) release from estuarine sediments response to warming. Combining field investigations and laboratory experiments, the study captured key ev...Read More